Email: Connect
Super streamlined.
#Functional #Pipeline #Control
A practical strategy for the modern brand.
Multiple aliases.
It can be a time-wasting hassle logging in & out of business email accounts on a computer, or just so exhausting scrolling through your emails accounts on your mobile phone. Centralising multiple email accounts on one system can increase performance while maintaining concentration. Diversify business email aliases and compartmentalise control.
Clutter Support.
A learning feature that automatically moves ignored messages to clutter box.
Exchange Level Search.
Configure your mailbox to sync, cached and index messages that you can directly search from your mailbox.
Setbody, Getbody, HTML-Inline.
Coupled with inline functions, setbody and getbody will make emails more reliable, while compatible with older email versions.
Focused inbox.
Most email services and clients have some sort of spam filtering capability. Microsoft Outlook detects non-spam yet non-important emails and filters these by reducing clutter.
File attachments.
Handling file attachments for mobile email just got a lot easier. When you tap the ‘files’ icon at the bottom of the mobile app, it will display recent file attachments in your email.
Cloud integration.
Outlook allows you to integrate OneDrive, Dropbox, Box, Google Drive, and other cloud storage accounts with the desktop app for quick access to all of your files.
Custom solution.
If the price seems too good to be true then it most likely is not a custom service. ProjektID provides quality bespoke solutions.
Brand asset.
Your business is only acquiring a solution to solve a problem you are also gaining the upper hand to surpass performance past your competitors.
Step-by-step.
Throughout a ProjektID service, you will be kept in the loop through the entire design and development of your branded solution.
Multifarious. Multifaceted.
Microsoft’s Outlook desktop and mobile app will enable business owners to streamline branded emails; because time is money and keeping your business straightforward can increase time efficiency, and in turn allow you to focus on increasing sales & profits. Having a platform that has a dynamic range of useful features will increase client satisfaction.

Problem-solving principles.
At ProjektID, we embrace 5 principles that allow us to provide a bespoke solution that solves your business’s problems. There is no cut and paste models in our services, only effective planning, developing, designing and implementation of work that provides your brand with meaningful value.
-
ProjektID can develop a strategy that works in tandem with your brand and the products/services that you provide to your customers/clients. First, we will engage in an intuitive workshop, which will allow both parties to deduce essential information about your business, including:
• Qualitative and quantitative industry data.
• Brand story and core unique characteristics.
• Goals and challenges.
• Strengths and weaknesses.
• Opportunities and threats.
-
Interacting with an existing audience is great for generating input. This can assist in focusing on perceptions of the products/services and the strategic B2B positioning too. Typical questions include:
• What do they like about your products/services?
• What benefits do they receive?
• Were they a customer/client of a previous business?
• Are there any recommendations for improvement?
-
The voice and personality of your brand are unique. Configuring these to flow throughout your whole business will avoid confusion. Hosting productive cross-functional meetings is an optimal method for integrating the brand positioning and mission statement together with:
• Strategies.
• Mock-ups.
• Copywriting.
• Online and offline operations.
• A guidelines dossier.
• An identity manual.
-
Your business’s target market share the same values, behaviours and personality traits as your brand. Now is the time to raise a community. A strong brand needs strong business assets, such as:
• Branded website development and designing.
• Powerful video marketing.
• Copywriting, social media and digital marketing.
• Graphic design assets.
-
When launching the business solution, developed and designed by ProjektID, you have a unique opportunity to decide how you wish to market your brand in the industry. Managing and maintaining the business assets is key for short-term and long-term growth. If the business assets are ignored then there is a potential for a collapse in performance.
Keeping an eye on the business’s assets metrics and feedback can control the execution of the launch and make adjustments if needed to achieve your brand’s objectives for the end-goal to stick the landing.
“Centralising yet compartmentalising day-to-day information will maintain and control simple to advanced business interactions”
Rough order Of magnitude.
A Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate (ROM estimate) is a ‘ballpark’ estimation of a project's scale and cost. ROM estimates are not representative of every project budget, rather a comprehension of the scope-to-budget ratio. Every project is unique and requires a particular range of solutions to assist a business in solving problems. Please do contact us to organise an initial meeting to discuss your project (scope, budget & timeline). Keep in mind that the price reflects the content, skill and technical complexity of this solution and in turn can generate better value for your business.
Medium Business
Approximate Duration: 1 Month
Small Business
Approximate Duration: 1 Month
Personal Business
Approximate Duration: 1 Month
€1,623.14
€660.03
€53.88
-
An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent or mail user agent (MUA) is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email. This is a software program specifically designed for composing, sending and receiving e-mail. Email client softwares include: Microsoft Outlook, Modzilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail an Inbox by Gmail. Access emails on desktop computer, laptop, tablet and smart phone devices.
-
An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent or mail user agent (MUA) is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email. This is a software program specifically designed for composing, sending and receiving e-mail. Email client softwares include: Microsoft Outlook, Modzilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail an Inbox by Gmail. Access emails on desktop computer, laptop, tablet and smart phone devices.
-
An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent or mail user agent (MUA) is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email. This is a software program specifically designed for composing, sending and receiving e-mail. Email client softwares include: Microsoft Outlook, Modzilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail an Inbox by Gmail. Access emails on desktop computer, laptop, tablet and smart phone devices.
-
In order to successfully setup your domain email accounts on an email client such as Mac Mail or Outlook, you will need to have the following information: Domain email address and password. Incoming mail server and port information. Outgoing mail server and port information. IMAP is the abbreviation for Internet Message Access Protocol. POP, short for the Post Office Protocol. An SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server sends, receives, and/or relays outgoing mail.
-
In order to successfully setup your domain email accounts on an email client such as Mac Mail or Outlook, you will need to have the following information: Domain email address and password. Incoming mail server and port information. Outgoing mail server and port information. IMAP is the abbreviation for Internet Message Access Protocol. POP, short for the Post Office Protocol. An SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server sends, receives, and/or relays outgoing mail.
-
In order to successfully setup your domain email accounts on an email client such as Mac Mail or Outlook, you will need to have the following information: Domain email address and password. Incoming mail server and port information. Outgoing mail server and port information. IMAP is the abbreviation for Internet Message Access Protocol. POP, short for the Post Office Protocol. An SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server sends, receives, and/or relays outgoing mail.
-
Email calendars are an excellent tool for maintaining & scheduling meetings, activities, events, and tasks. Organizing daily, weekly, and monthly calendars in a single place can allow the user to see the big picture of the schedule in just a few clicks. This allows for optimising work time and in turn enhances business performance.
-
Mail contacts are mail-enabled objects that contain information about people who exist outside your organization. Each mail contact has an external email address. For more information about mail contacts, see Recipients in Exchange Online.
-
The guidelines dossier outlines a set of rules for the brand to abide by in order to maintain a high level of quality with the business asset.
-
For better account security, set up 2-step verification (2SV), also known as Multi-factor authentication (2FA). This is an electronic authentication method in which a device user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism: knowledge, possession, and inherence. Gain assistance with enhancing log-in security in an email account, and protect confidential correspondence.
-
Throughout the project, receive ongoing & regular technical consultations. Gain an in-depth understanding of the project & phases, business asset(s), and strategic & technical guidance that assists your brand.
-
Once a project is complete and 100% of the budget is fullfiled, a certificate of ownership will be provided.
Service roadmap.
Comprehending the complete development processes is key in maximising the performance of a project’s success. ProjektID works in tandem with clients in order to maintain operational control of every single detail.
-
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
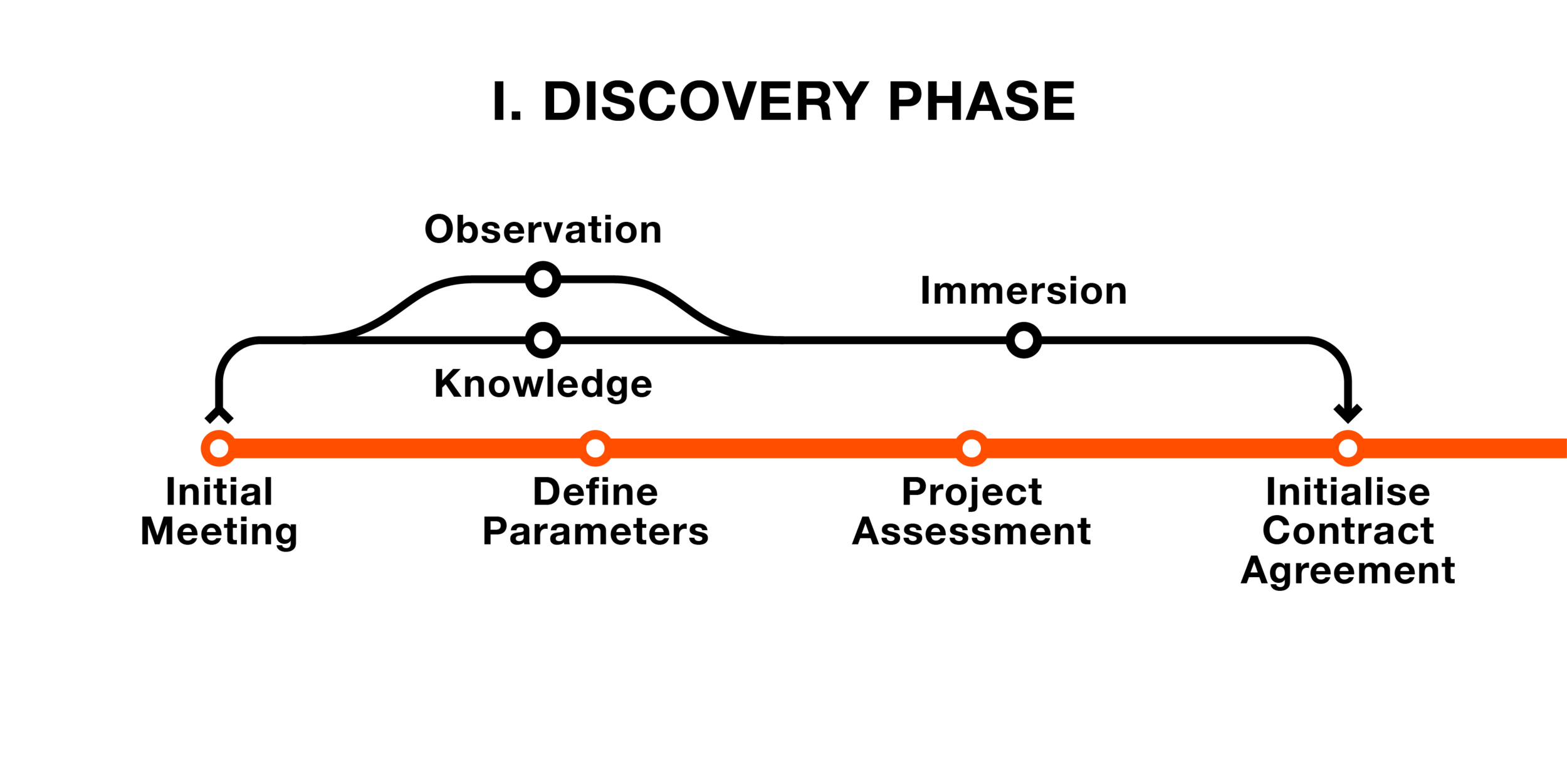
Discovery Phase
In the Discovery phase, ProjektID will need to initially define the scope of the project. This is done through an initial meeting with the client. Then the project parameters can be defined along with an assessment of the project. Once all of this is complete, the project ‘Authorisation To Proceed’ (ATP) Contract will need to be agreed to and the project will commence.
-
Approximate Duration: 17 Days
Approximate Duration: 8 Days
Approximate Duration: 8 Days
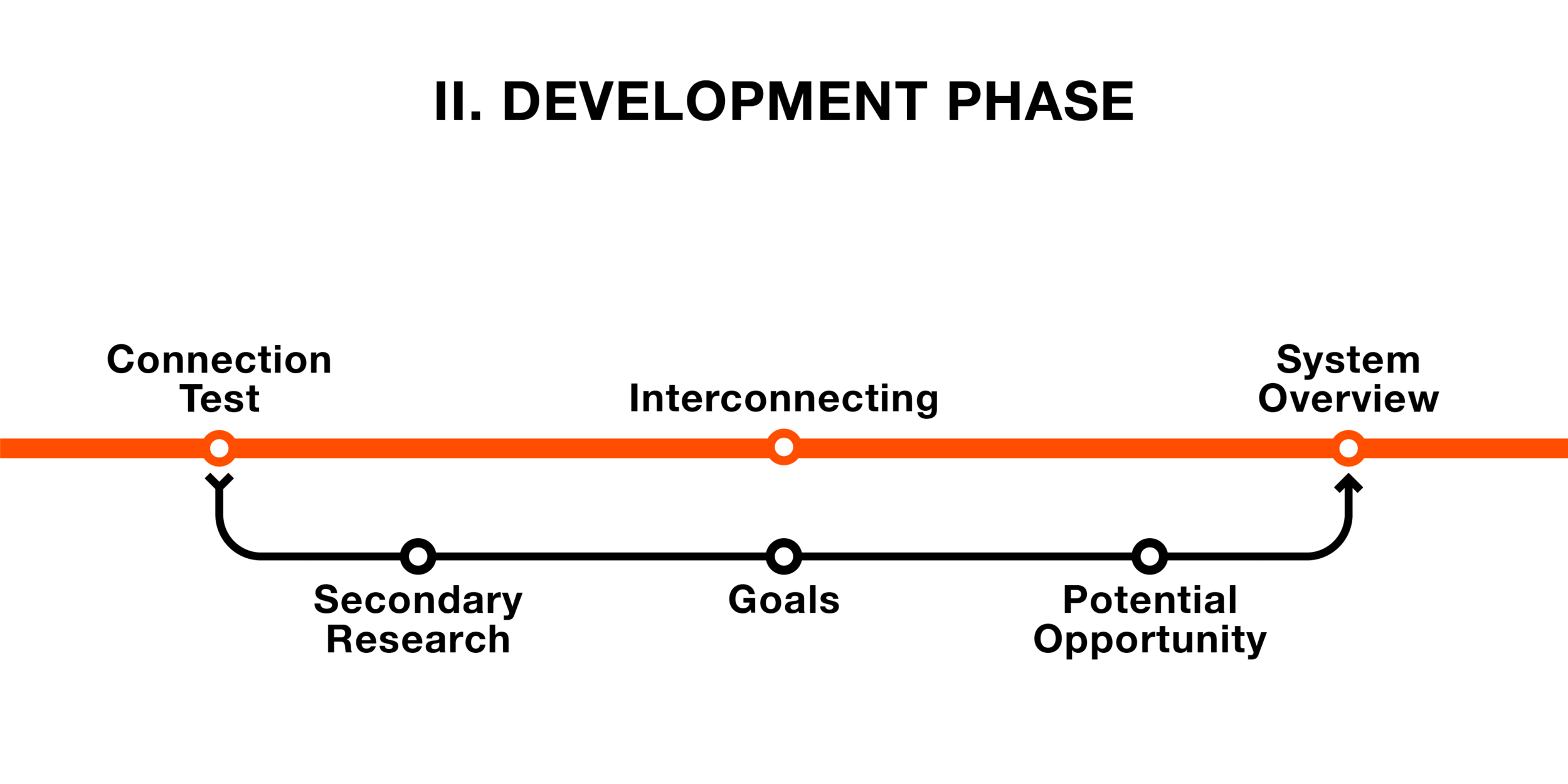
Development Phase
In the Development phase, the solution will undergo creation. A demonstration live model will then be created. All of these will be displayed to the client for feedback and agreement.
-
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
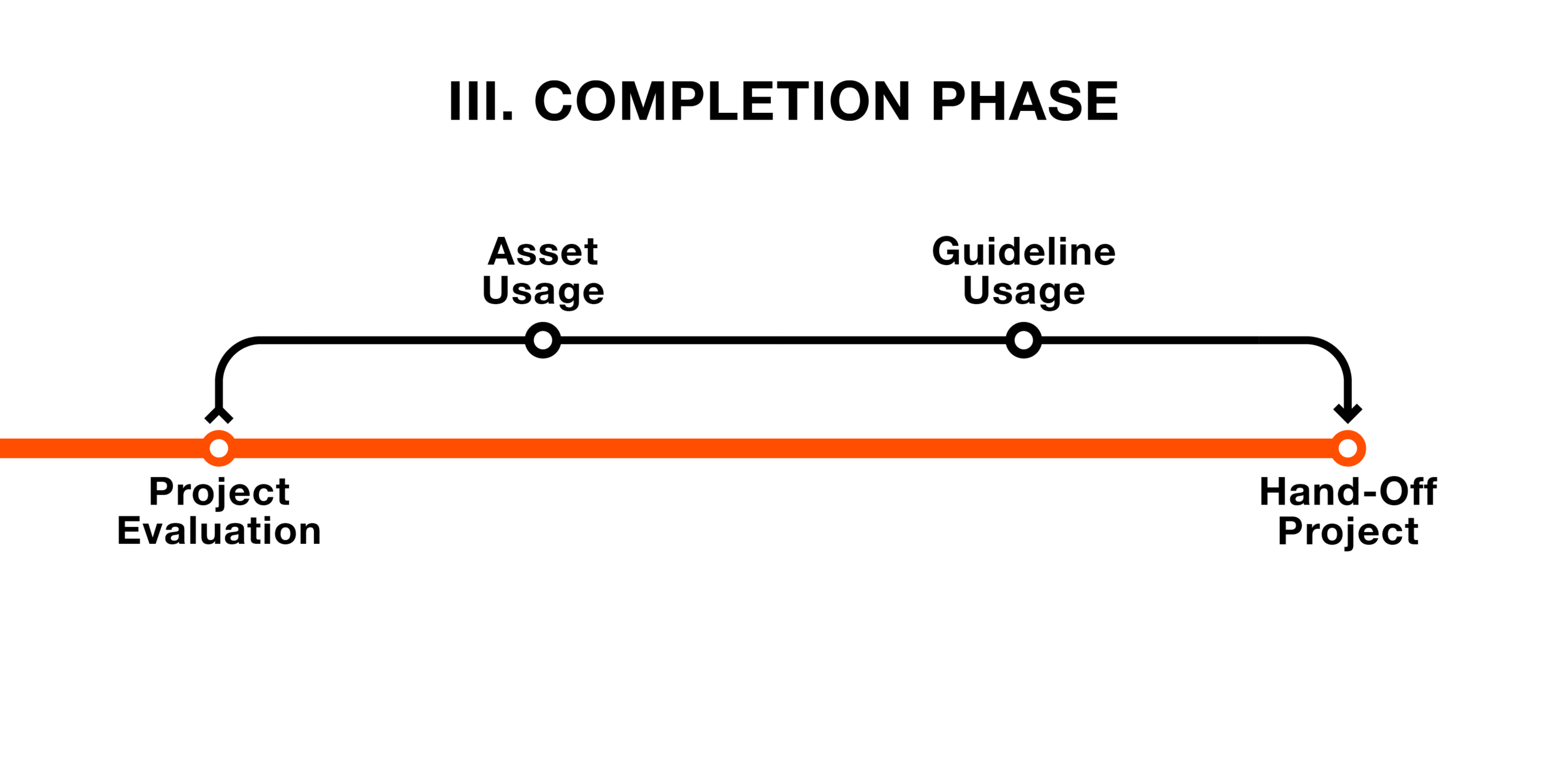
Completion Phase
In the Completion phase, both ProjektID and the client will evaluate the project together. Once the project has fulfilled the objectives in the whole project scope, the project will be handed off to the client.
Project glossary.
A glossary is an alphabetical list of terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms.
Budget
The amount of money that a person, group, or organization has available to spend on a ‘project’. A budget defines the maximum and minimum values allocated to generate a particular outcome.
Project
A piece of planned work or activity that is completed over a period of time and intended to achieve a particular aim.
Project Complexity
The condition of lacking simplicity of a problem. A set of problems that consists of many parts with a multitude of possible interrelations, being of high consequence in the decision-making process that brings about the final result.
Project Scale
A determining factor from ‘Project Scope’, is most simply defined as the degree and extent to which project management practices are formally applied. Taking a "one size fits all" approach is unwise and impractical.
Project Scope
Features and functions of the scope of work needed to complete a project. Scope involves gathering information required to initialise a project, and the features the project would have that the client requires.
Project TimeLine (Duration)
A period of seconds, minutes, days, hours, weeks, months, or years, in which something may happen or in which something may occur.
Quality Control (QC)
This is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved. Quality control requires creating an environment in which a project strives for perfection.
Roadmap
Provides a strategic overview of the major elements of a project. This usually includes objectives, milestones, deliverables, resources, and a planned timeline.
Service Element Deliverable (SED)
A sub-division of Project Scope, a Service Element Deliverable is an action that is performed within a specific aspect of a project in order to serve a purpose. Multiple actions together (SEDs) compose the scope of work.
Stage (Phase)
A collection of activities within a project. Each project phase is goal-oriented and ends at a milestone. Reaching these milestones means the project progresses. Each phase can be divided into sub-phases.
Stage (Plan)
These include things to do, short-term and long-term objectives, and other actions that affect project completion.
Stage (Progress)
These include milestones, goals achieved, finished tasks and validated items that contribute to project completion.
Variable
A variable is any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types. A project usually has three kinds of variables: independent, dependent, and controlled.
Variable (Control)
A control variable, or constant, in project development is an element which is constant and unchanged throughout the course of the project. The control variables themselves are not altered throughout any project scale.
Variable (Dependent)
The variable is measured during project development and is 'dependent' on the independent variable. In a project, the effect on the dependent variable is caused by altering the independent variable.
Variable (Independent)
The variable being manipulated during project development and is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable. This determines the cause and effect of a project.
Project scale.
‘Project Scale’ is a determining factor from ‘Project Scope’ and ‘Project Complexity’, most simply defined as the degree and extent to which project management practices are formally applied. It is unwise and impractical to take a ‘one size fits all’ approach to each project, as there will be unique problems to solve along with varying scales, scopes and complexities to assess.
Project Scale = Project Scope X Project Complexity
Project variable.
A variable is any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types. A project usually has three kinds of variables: independent, dependent, and controlled.
Control Variable
The control variable, or constant, in project development is an element that is constant and unchanged throughout the course of the project. The control variables themselves are not altered throughout any project scale.
Quality Control
Independent Variable
The dependent variable is what gets measured during project development, and is 'dependent' on the independent variable. In a project, the effect on the dependent variable is caused by altering the independent variable.
Timeline
Dependent Variable
The independent variable is what gets manipulated during project development, and is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable. This determines the cause and effect of a project.
Budget
Our projects.
Developing a specific strategy for a business in a unique situation, within both the digital and physical world, has allowed us to vary our mindset to solve specific problems. Take a peek at some projects that we have been excited to work on.